Key information
Electromagnetic radiation consists of waves, the majority of which are invisible.
Only one small part of this type of radiation can be identified by the human eye, and that is the visible light which
produces the various colors of the rainbow.
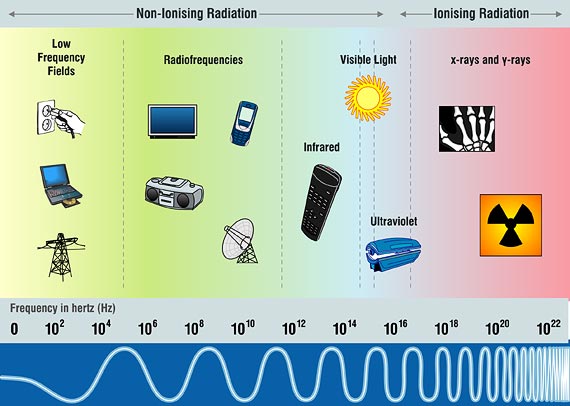 |
| Diagram 1 - Electromagnetic Spectrum |
Electromagnetic fields are generated across a wide spectrum of frequencies (known as the electromagnetic spectrum) which
is divided into specific frequency bands or zones (Diagram 1). The frequency spectrum includes ionizing and non-ionizing radiation.
Ionizing radiation has a frequency higher than visible light. It has a smaller wavelength and carries high quantities of energy.
Ionizing radiation includes cosmic radiation, X-rays and radioactive α-decay, β-decay and γ-rays. It is called "ionizing"
because it causes matter to ionize, in other words -to use scientific terminology- the photon of the radiation carries so much energy
that it can remove an electron from an atom of matter. This radiation can cause immediate harm to biological matter, particularly cell
DNA.
The sources of electromagnetic fields, which we are daily exposed to (radio waves, microwaves, electricity) have high
wavelengths and low frequencies. They cannot cause ionization, because they carry low quantities of energy. They cannot break the chemical
bonds in cell molecules.
Electromagnetic fields generated by electricity cables and household appliances have exceptionally low frequencies
reaching only 300 Hz max. Radio frequencies are located between 10 MHz and 300 GHz.
Electromagnetic fields are to be found everywhere in the environment and come from either natural or artificial sources.
The Earth's electromagnetic field, sunlight, lightning, heartbeats, and the human central nervous system are all natural sources of
electromagnetic fields. Artificial sources include household appliances (vacuum cleaners, microwaves, refrigerators, televisions, etc.),
electricity cables, television and radio stations, mobile telephony base stations, radars and so on (Diagram 2).
 |
| Diagram 2 - Sources of Electromagnetic Radiation |
It should be noted that the existence of electromagnetic fields causes electric current. Electromagnetic fields can be
of high or low strength, continuous or short-term.
Electromagnetic fields are generated due to the difference in electric potential. The higher the potential
difference, the stronger the electric field generated. The measurement unit of electric field strength is the Volt per meter (V/m).
Magnetic fields are generated wherever current flows. The higher the current intensity, the greater the strength
of the magnetic field. When the current is turned off, the magnetic field drops away. An appliance, like a hairdryer for instance,
produces a magnetic field only when plugged in and turned on. When the current is turned off, the magnetic field drops away.
The measurement unit of magnetic field strength is the Ampere per meter (A/m).
| 